
In the realm of precious stones, diamonds hold an unrivaled position, their enchanting fire and brilliance captivating admirers for centuries. But what defines a diamond's true worth and beauty? The answer lies in the 4Cs: a meticulous grading system established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). This system objectively evaluates and grades diamonds based on four essential criteria. Each "C"—cut, color, clarity, and carat weight—plays a vital role in creating a diamond's radiance, serving as fundamental benchmarks for any professional diamond assessment.
•‧•┈┈┈┈୨୧┈┈┈┈•‧•

CUT
Cut pertains to the proportions and angles of a diamond's facets, significantly influencing its brilliance and sparkle. A diamond with an excellent cut will reflect the maximum amount of light that enters it, resulting in a stunning display of fire and scintillation.
THE KEY TO LIGHT PERFORMANCE
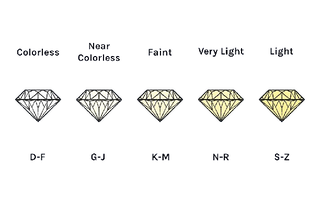
COLOR
Color indicates the degree of color present or absent in a diamond. Diamonds are assessed on a scale from D (completely colorless) to Z (noticeable light yellow or brown). Typically, diamonds closer to the colorless end of the scale are more prized and valuable. A colorless diamond allows more light to pass through, enhancing its brilliance and overall appeal. In contrast, diamonds with more color may appear less bright and radiant. The subtle variations in color can significantly impact the diamond's value and aesthetic.
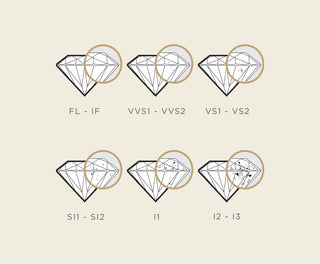
CLARITY
Clarity describes the extent of internal and external imperfections, known as inclusions and blemishes, within a diamond. These flaws, which can include cracks, crystals, or cloudy areas, may affect the diamond's brilliance and visual appeal. Diamonds undergo grading on a scale from Flawless (FL), indicating no visible flaws under 10x magnification, to Included (I), where inclusions are noticeable to the naked eye. The clarity grade of a diamond reflects its purity and rarity, with flawless diamonds commanding higher value due to their pristine appearance.
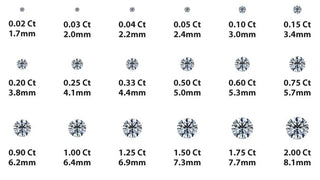
CARAT
Carat denotes the size and weight of a diamond, measured in metric carats where one carat equals 200 milligrams. Although carat weight typically influences a diamond's price, it's crucial to consider the other aspects of the 4Cs—cut, color, and clarity. While a larger diamond may seem more valuable at first glance, its worth can be diminished if it lacks superior cut or clarity. Conversely, a smaller diamond with exceptional cut and clarity may possess greater value and allure. Therefore, when evaluating diamonds, it's essential to strike a balance between carat weight and the quality of the other Cs to ensure optimal beauty and value.




